AMR
Action &
Insights
AMR Action & Insights will explore how we mitigate the impact of antimicrobial resistance in Australia and beyond.
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) and Australia
AMR Action & Insights explores the complexity of AMR through a One Health lens, with a specific focus on Australia.
AMR is a global health concern affecting all sectors – but that doesn’t mean the situation is the same in every country.
So how does the situation in Australia differ from elsewhere in the world? In what ways are we better, or worse? And what advantages do we have that others don’t?
Latest articles:
Ramping up the fight against bacteria to prevent devastating neonatal sepsis
Accelerating AI to search for new antibiotics
How do bacteria actually become resistant to antibiotics?
What is a One Health approach to antimicrobial resistance?
Community control key to reducing AMR in Australia

Human health and AMR
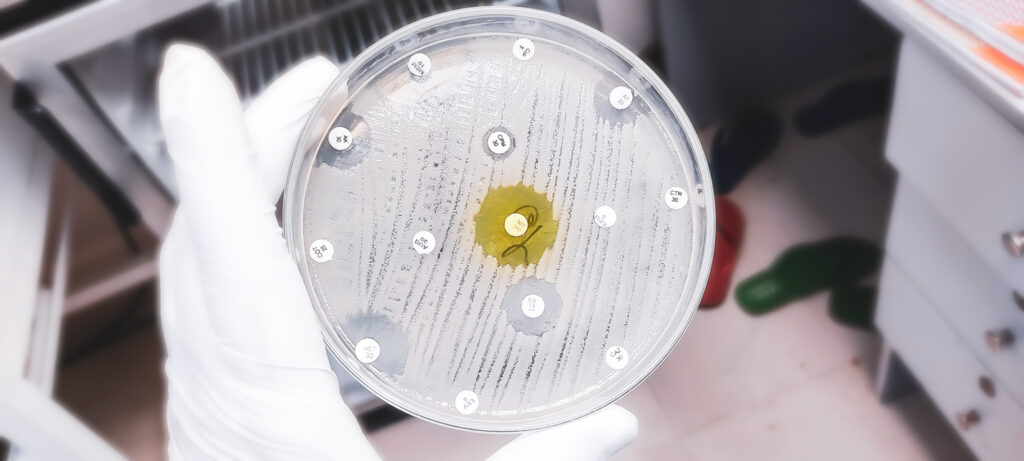
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a profound threat to human health, undermining the efficacy of antibiotics that have been the cornerstone of modern medicine.
As bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites evolve to resist the effects of medications, common infections become harder to treat, leading to longer illnesses, higher medical costs, and increased mortality.
Animal health and AMR
AMR is a major emerging issue in animal health, for both production and companion animals.
However many of the assumptions about the use of antimicrobials in food production in Australia are incorrect, and informed by perceptions in overseas industries.


Environment and AMR
The environment is somewhat overlooked when it comes to antimicrobial resistance. Yet AMR can spread within the environment through water, wastewater, animal manure, and food.
One Health
The One Health approach recognises that the health of humans, animals, and the environment are interconnected.
AMR is a critical issue that spans these domains and which requires a collaborative effort to mitigate its impact.