Home /

Human health
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a profound threat to human health, undermining the efficacy of antibiotics that have been the cornerstone of modern medicine.
As bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites evolve to resist the effects of medications, common infections become harder to treat, leading to longer illnesses, higher medical costs, and increased mortality.
-
Accelerating AI to search for new antibiotics
CSIRO experts are using artificial intelligence (AI) in the search for new antibiotics and say it will lead to a better hit rate of successful pharmaceutical candidates.
-
How do bacteria actually become resistant to antibiotics?
Contrary to a common belief, antibiotic resistance is not about your body becoming resistant to antibiotics.
-
Making sense of AMR data
Understanding and linking data between animals, humans and the ecosystem.
-
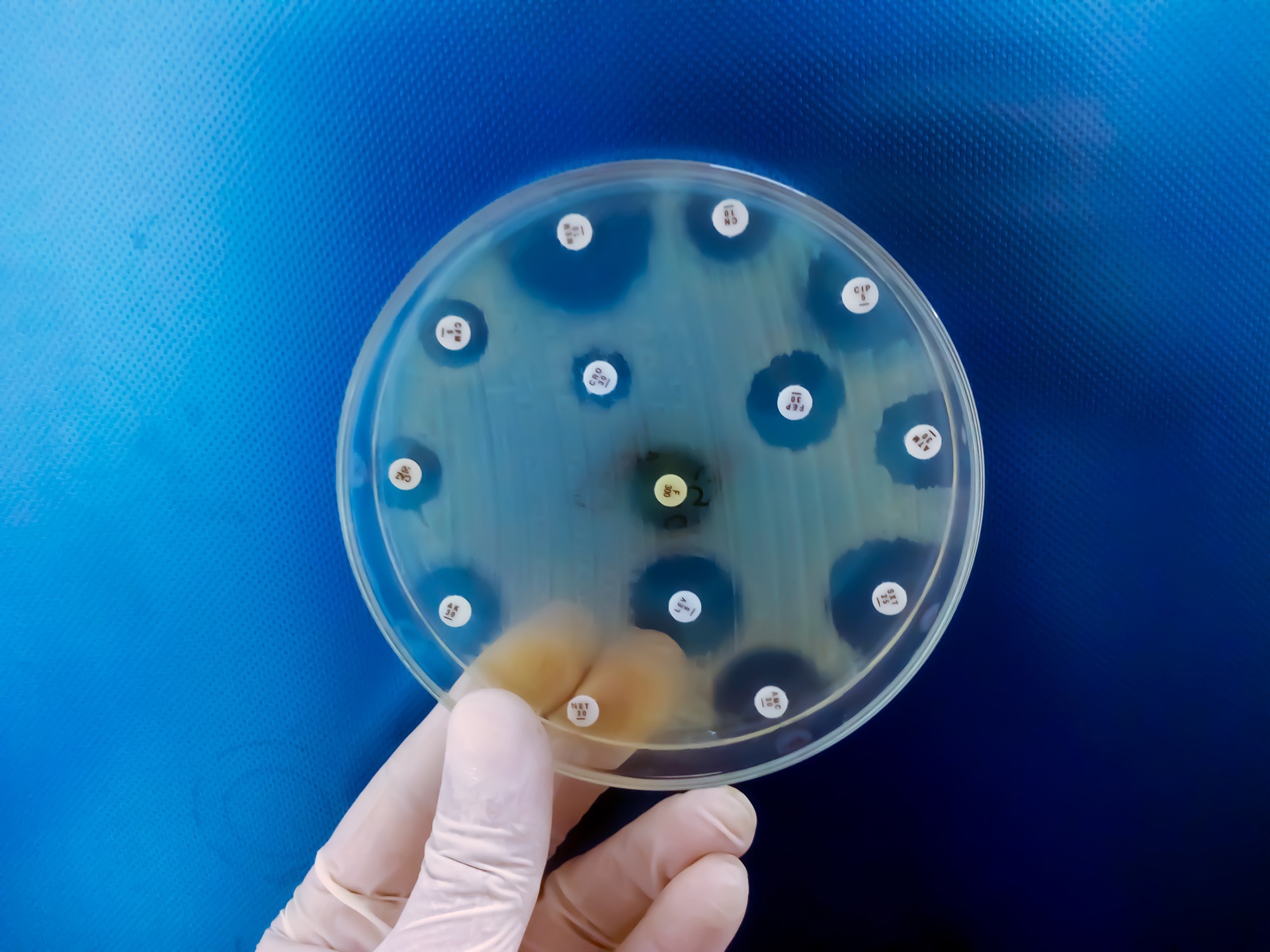
A One Health approach to antimicrobial resistance
A comprehensive One Health approach addresses the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health.
-

Community control key to reducing AMR in Australia
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander community controlled health organisations take a different approach from the mainstream health system, with impressive results.
-

Explainer: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR)
AMR occurs when microbes, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites evolve to resist the drugs designed to kill them, rendering treatments ineffective.
-

How vaccines can help mitigate AMR
Next-gen vaccines targeting bacterial infections will take the pressure off antibiotics.
-
AI a potential game-changer for antibiotic drug development
AI Machine Learning could potentially unblock the antimicrobial drug development pipeline.
-

Six strategies to minimise AMR in Australia
Six key ways that Australia can shore up its antimicrobial stewardship, including optimising antimicrobial use and increasing education.
-

Patients have a common enemy in AMR
The rise of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a growing concern for patients who are immunosuppressed and predisposed to infections.