Home /

Environment
The environment plays a key role in the spread of antimicrobial resistance. Environmental factors, such as pollution and waste management, contribute to the persistence and spread of resistant organisms, influencing the broader AMR landscape.
-
What is a One Health approach to antimicrobial resistance?
A comprehensive One Health approach addresses the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health.
-

Explainer: What is Antimicrobial Resistance? (AMR)
AMR occurs when microbes, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites evolve to resist the drugs designed to kill them, rendering treatments ineffective.
-
Australia’s edge: Minimising AMR down under
Australia is well-positioned in the global effort to combat AMR.
-
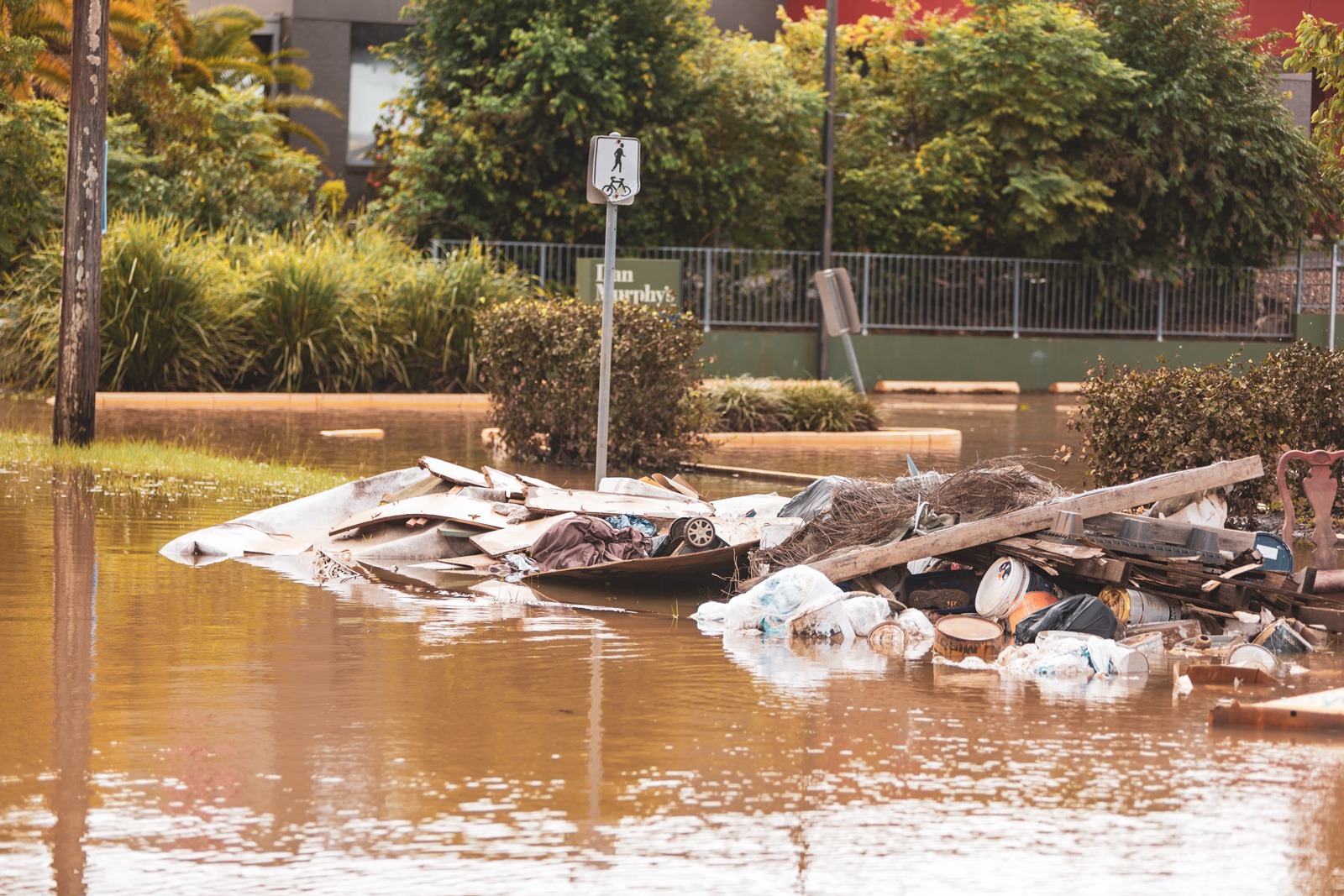

Is climate change exacerbating AMR?
Higher temperatures, flooding and other natural disasters have implications for AMR.
-
Explainer: how does AMR happen?
Microbes are survivors, hardwired to fight back against enemies that include antibiotics.